Infectious diseases are a major health concern in Liberia. Some of these diseases are transmitted through
- Contaminated water
- Poor sanitation
- Close contact
Communities and individuals can be protected by understanding their causes, symptoms and preventative measures. This article explores common infectious diseases in Liberia and how it takes an active community to prevent them.
1. Malaria
Malaria is the leading cause of mortality in Liberia. It spreads through the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito. It is caused by the plasmodium parasite.
Symptoms

- Chills and fever
- Sweating and headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Muscle pain and fatigue
- Headache
- Joint Pains
Prevention
- Antimalarial medications, artesunate
- Take antimalarial prophylaxis medications doxycycline
- Use mosquito repellants
- Draining of stagnant water
- Sleeping under mosquito-treated nets
2. Tuberculosis (TB)
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by a bacteria known as Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Although it can spread to other organs, it primarily affects the lungs. It spreads when infected individuals cough or sneeze, releasing TB particles into the air.
Symptoms
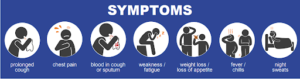
- Chronic persistent cough for more than two weeks
- Difficulty in breathing
- Chest pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Night sweats
Prevention
- Get the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine
- Anti-TB drugs
- Good ventilation at home and in the office places
- Coughing and sneezing etiquette
- Health education
- Community awareness
3. Cholera
Cholera is caused by Vibrio cholerae bacteria, which leads to severe diarrheal illness. If untreated, it can cause dehydration and even death. It spreads through contaminated
- Water
- Food
Symptoms
- Muscle cramps and weakness
Vomiting and dehydration - General body malaise
- Watery diarrhea
Prevention
- Use proper sanitation and dispose of waste safely
- Isolation of affected patients
- Treatment of affected patients: boil water before drinking
- Wash hands with running water and soap
- Avoid street food
- Proper cooking of food
4. Lassa Fever
Lassa fever is spread by rodents. It’s an aviral infection, and individuals get infected through contact with rodent urine, saliva, and feces. It can also spread from person to person through body fluids.
Symptoms
- Cough
- Fever
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Bleeding
- Organ failure
Prevention
- Follow infection control measures in healthcare settings
- Avoid contact with infected individuals
- Food should be stored in rodent-proof containers
- Keep homes clean and clear bushes
- Use anti-rodent traps and bait
- Isolation of infected individuals
5. Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B involves the inflammation of the liver by a viral infection. It spreads through infected body fluids, sexual contact, and also transplacental transmission (passing to the baby while pregnant).
Symptoms
- Jaundice
- Hepatomegaly
- Dark urine
- Pale stool
- Fatigue
- Ascites
- Lack of appetite
Prevention
- Get vaccinated against Hepatitis B
- Use condoms during sexual intercourse
- Avoid sharing sharp tools
- Avoid sharing personal hygiene items
- Screen blood before transfusion
6. Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever is caused by the Salmonella typhi bacteria. Poor sanitation increases the risk of infection, also spread through contaminated food and water
Symptoms
- Diarrhea
- High fever
- General body malaise
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
- Confusion
- Vomiting
Prevention
- Drink treated water
- Eat properly cooked food
- Wash hands before and after eating
- Wash hands after using toilet
7. HIV/AIDS
The body’s immune system is weakened by HIV, leading to opportunistic infections. One gets infected through unprotected sex, mother-to-child transmission during delivery, and contact with infected blood.
Symptoms
- Weight loss due to persistent infectious
- Night sweats
- Lymphadenopathy
- Flu in early stages
- AIDS in advanced stages weakens immunity
Prevention
- Take antiretroviral therapy (ART) if infected.
- Use protection during intercourse like condoms
- Take Antiretroviral therapy
- Don’t share sharp tools like needles or razors
- Regular screening
- Health education
8. Ebola Virus Disease
One of the killer viral diseases is Ebola. Healthcare workers are at high risk. The disease spreads through contact with the bodily fluids of infected animals or individuals.
Symptoms
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Hyperthermia
- General body malaise
- Excessive uncontrolled bleeding
- Multiorgan failure
Prevention
- Proper hygiene measures
- Wear protective gears like gloves, gumboots, uproans
- Avoid contact with infected animals
- Proper cooking of meat
- Isolation of infected patients
- Don’t consume meat from the bush
9. Measles
Measles is an airborne disease that spreads when infected individuals cough or sneeze, releasing infected droplets in the air. Thus, it spreads easily.
Symptoms
- Cough and high fever
- Red eyes
- Running nose
- Rashes on the face, spreading downwards
Prevention
- Get the measles vaccine
- Avoid close contact with infected individuals
- Practice good hygiene and regular handwashing
10. Yellow Fever
Yellow fever affects the liver and other organs. It spreads through mosquitoes that carry the virus. Severe cases can lead to internal bleeding and organ failure.
Symptoms
- Fever and chills
- Jaundice
- Dark urine
- Nausea
- Bleeding from the nose, mouth, or stomach in severe cases
- vomiting
Prevention
- Be vaccinated for yellow fever
- Use insect repellents
- Wear protective clothing
- Remove mosquito breeding sites
General Prevention Strategies
Although each disease has its prevention measures, there are some general measures of protection against infections.
- Maintain Good Hygiene
- Practice regular hand washing with soap and water
- Where soap is unavailable, carry hand sanitizers
- Improve Sanitation
- Use clean and safe toilets
- Dispose of waste properly
- Ensure Safe Drinking Water
- Before drinking, either boil or treat water
- Store water in clean, covered containers
- Get Vaccinated
- Follow the recommended vaccination schedule
- Keep vaccination records up to date
- Practice Safe Food Handling
- Always wash fruits before eating
- Cook meat and seafood thoroughly
- Prevent Mosquito Bites
- Sleep under treated mosquito nets
- Use mosquito repellents
- Wear protective clothing
- Seek Medical Care Early
- If you are symptomatic, visit a healthcare facility
- Do not self-medicate with unprescribed drugs
Conclusion
Liberia continues to face a major public health threat from infectious diseases. But most can be prevented by proper hygiene, vaccination and healthcare. Costs can be saved in communities through adopting preventative measures.
You can make a difference and help prevent the spread of infectious diseases throughout Liberia with your support of LMI.
Liberia Medicals Inc. aims at promoting health and prevention of disease in Liberia. For more information on how you can have a deep impact on healthcare services and disease prevention programs, contact us.